Understanding the Mechanics of Universal Life Insurance
How does universal life insurance work? Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance where your premium is split into two parts: one pays for the cost of insurance (death benefit, fees, and administrative charges), and the other goes into a cash value account that grows tax-deferred based on an interest rate set by the insurer. You can adjust your premium payments and death benefit over time, and you can access the cash value through loans or withdrawals—but if the cash value runs too low, your policy could lapse.
Here’s the basic flow:
- You pay premiums → Part covers insurance costs, part builds cash value
- Cash value grows → Earns interest (with a guaranteed minimum rate)
- You have flexibility → Adjust premiums up/down or skip payments (if cash value is sufficient)
- You can access funds → Borrow or withdraw from cash value while living
- Death benefit pays out → Beneficiaries receive a tax-free payout when you pass
The key difference from whole life is flexibility—you control how much you pay and when, but that also means you need to monitor your policy to prevent it from running out of cash value. Unlike term life, which expires after a set period, universal life is designed to last your entire lifetime as long as you keep it funded.
At ShieldWise, we’ve guided countless families and retirees through the complexities of permanent insurance, helping them understand exactly how does universal life insurance work and whether it fits their long-term goals. We break down the jargon and give you the tools to make informed decisions without the sales pressure.
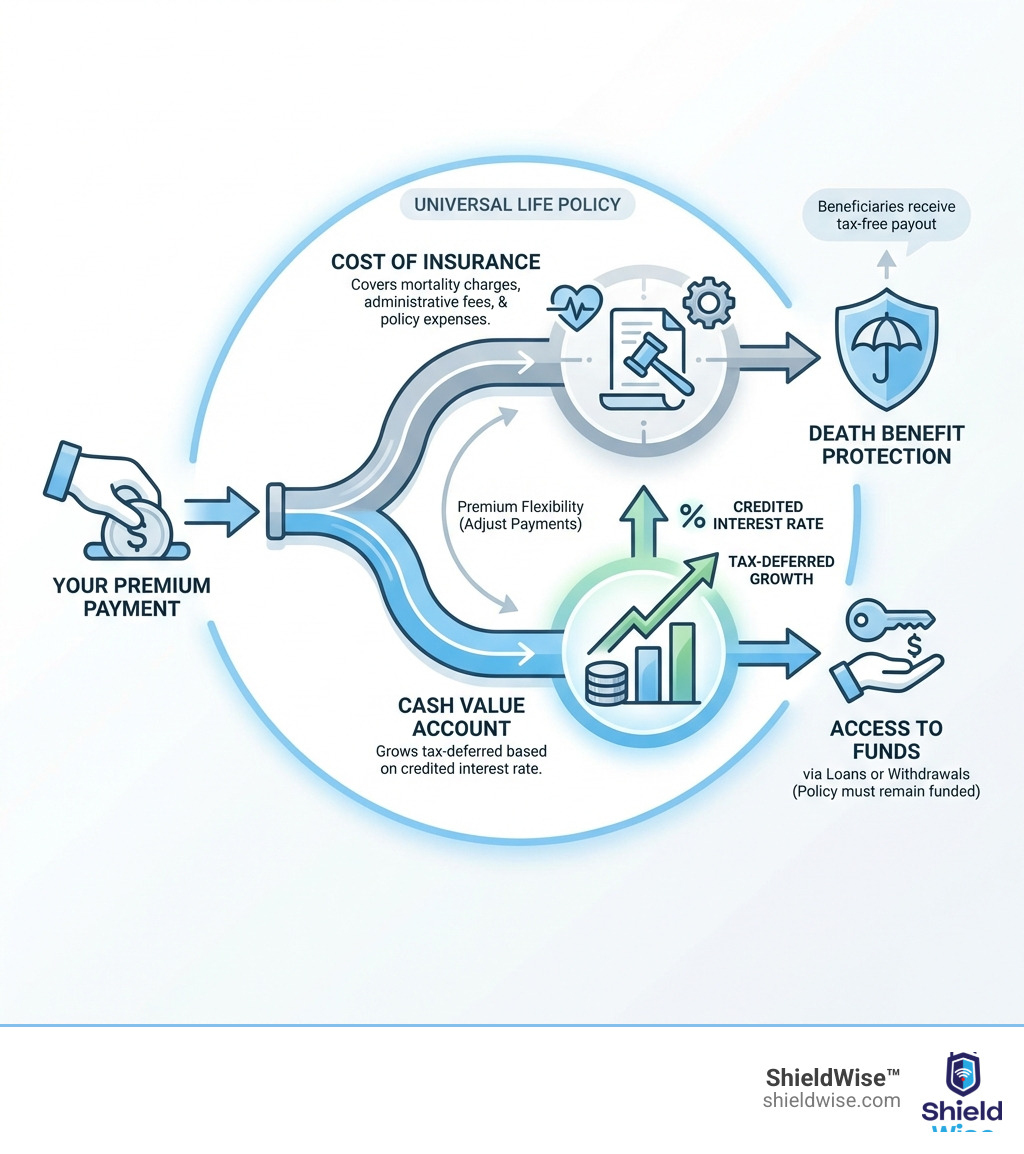
What is Universal Life Insurance?
Universal life (UL) is permanent life insurance with two parts working together:
- A guaranteed death benefit designed to last for life, as long as the policy stays funded.
- A cash value account that grows tax-deferred and can be accessed while you’re alive.
Unlike term life, UL doesn’t end after 10–30 years. Unlike whole life, UL lets you adjust premiums and, within limits, the death benefit. That flexibility makes UL a powerful financial tool for estate planning, business continuity, or simply creating options later in life.
Key features:
- Permanent coverage if kept in force
- Adjustable premiums and death benefit
- Tax-deferred cash value growth
- Access to cash via policy loans or withdrawals
- Potential to customize for families and business owners
To see where universal life fits among your options, explore our overview on Universal Life for Families and Protection.
How Does Universal Life Insurance Work?
At a high level, every UL policy follows the same mechanics:
- You pay a premium.
- The insurer deducts monthly policy charges—mortality charges and expenses, known collectively as the cost of insurance (COI).
- The remainder goes to your cash value.
- The cash value earns interest—either a set rate, an index-based rate, or market performance, depending on policy type.
- If your cash value is sufficient, you can reduce or skip payments temporarily. If it’s not, you must pay more to keep coverage active.
The Main Components of a Universal Life Premium
- Cost of Insurance (COI): Covers mortality charges based on your age, health, and risk class. COI rises with age.
- Administrative fees and policy expenses: Monthly or annual charges for managing the policy.
- Cash value contribution: Whatever remains after charges is credited to your cash value.
- Minimum premium: The lowest amount needed to keep the policy from lapsing in the short term.
- Target premium: A recommended level designed to cover projected costs and help cash value grow so the policy stays healthy over time.
For a deeper primer, see our plain-English walkthrough, What Is Universal Life (UL) Insurance?.
How the Cash Value Component of Universal Life Insurance Grows
- Credited interest rate: In traditional UL, the insurer sets a rate, often with a small guaranteed minimum. In indexed UL (IUL), returns are tied to an index with caps and floors. In variable UL (VUL), your returns depend on invested sub-accounts you choose.
- Minimum guaranteed rate: Most UL designs include a floor so credited interest never drops below a minimum; IUL often includes a 0% floor for negative index years.
- Tax-deferred accumulation: Cash value grows tax-deferred. Taxes apply when you withdraw gains or if the policy becomes a MEC (more on that later).
- Overfunding: Paying more than the minimum premium builds cash value faster, which can support lower payments later and help avoid lapse.
Learn more about building and using cash value in our guide, Universal Life Cash Value and Flexibility.
Can You Adjust Premiums and Death Benefits with Universal Life Insurance?
Yes—this is UL’s superpower.
- Premium flexibility: You can increase, decrease, or even skip payments temporarily as long as there’s enough cash value to cover monthly COI and fees.
- Death benefit options:
- Option A (Level): Keeps the death benefit level. As cash value increases, the net amount at risk for the insurer decreases.
- Option B (Increasing): Death benefit equals the base amount plus your cash value. This costs more but preserves your built-up equity for beneficiaries.
- Underwriting: Increasing the death benefit or making certain changes may require new underwriting.
Can You Borrow Against or Withdraw from the Cash Value?
- Policy loans: Typically tax-free while the policy stays in force. Interest accrues, and any outstanding loan reduces the death benefit dollar-for-dollar.
- Withdrawals: Reduce cash value and may reduce the death benefit. Amounts above your basis (total premiums paid minus previous withdrawals) are taxable as ordinary income.
- Surrender charges: Many policies have surrender periods with charges if you cancel early.
- Tax note: If your policy becomes a Modified Endowment Contract (MEC), loans and withdrawals are taxed as gain-first and may face a 10% penalty if you’re under age 59½.
If you’re considering IUL, see how borrowing works in practice in How IUL Loans Work.
What are the Different Types of Universal Life Insurance?
Universal life comes in several flavors. Picking the right one depends on how much risk, flexibility, and guarantee you want.
- Traditional or Fixed UL: Cash value earns an insurer-declared rate with a guaranteed minimum.
- Indexed UL (IUL): Credits interest based on an equity index, with caps and floors.
- Variable UL (VUL): Invests in market sub-accounts you select; values can go up or down.
- Guaranteed UL (GUL): Emphasizes guaranteed lifetime coverage with minimal cash value.
Indexed Universal Life (IUL)
IUL links credited interest to an index such as the S&P 500, using a formula:
- Participation rate: The percentage of index gains your policy credits.
- Cap: The maximum annual crediting rate.
- Floor: The minimum, often 0%, protecting against negative index years.
IUL aims to balance upside potential with downside protection. Dive into the mechanics in How Does IUL Work and the broader overview What is IUL.
Variable Universal Life (VUL)
VUL invests your cash value in sub-accounts similar to mutual funds:
- Higher risk, higher potential growth
- No caps or floors—market losses can reduce cash value
- You control allocation among stocks, bonds, and other assets
Learn the essentials in What Is Variable Universal Life?.
Guaranteed Universal Life (GUL)
GUL is built to deliver lifetime coverage at a lower cost, typically with:
- A strong no-lapse guarantee tied to paying scheduled premiums
- Minimal emphasis on cash value growth
- A focus on the death benefit, not accumulation
See how this compares to term and other permanent options in Universal Life Term Versus Permanent.
How Does Universal Life Insurance Compare to Other Policies?
Here’s a quick side-by-side to clarify where UL fits.
| Feature | Term Life | Whole Life | Universal Life |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage Duration | 10–30 years | Lifetime | Lifetime |
| Premium Cost | Lowest | Highest | Mid-to-high |
| Premium Flexibility | None (level) | None (level) | High (adjustable) |
| Cash Value | None | Guaranteed growth | Variable growth by policy type |
| Best For | Pure income replacement | Guarantees and simplicity | Flexibility and control |
Universal Life Insurance vs. Whole Life Insurance
- Premiums: Whole life has fixed premiums; UL premiums are adjustable.
- Cash value: Whole life grows at guaranteed rates and may earn dividends. UL growth varies (fixed, indexed, or market-based).
- Control: Whole life is simpler and more “set it and forget it.” UL requires monitoring but offers more levers to pull.
Universal Life Insurance vs. Term Life Insurance
- Duration: Term is temporary; UL is designed to last for life.
- Cash value: Term has none; UL builds cash value you can access.
- Cost: Term is often the most affordable way to buy a large death benefit. UL costs more but offers flexibility and living benefits.
For a deeper comparison, see our Universal Life Insurance Guide 2026.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Universal Life Insurance?
Advantages of Universal Life Insurance
- Flexible premiums to fit changing cash flow
- Adjustable death benefit to match evolving needs
- Tax-deferred cash value growth
- Access to cash via loans and withdrawals
- Permanent coverage if adequately funded
- Multiple policy types to match your risk tolerance
Disadvantages of Universal Life Insurance
- Complexity—requires ongoing monitoring and periodic adjustments
- Rising COI with age can erode cash value if underfunded
- Fees and charges reduce returns
- Investment risk in IUL/VUL can lead to lower-than-expected growth
- Risk of lapse if cash value is depleted or premiums are insufficient
- Insurer strength matters—always check ratings with AM Best
A sobering data point often cited in industry analyses: nearly 88% of universal life policies never pay out due to lapses—usually from underfunding, rising costs, or policyholders losing track of performance. That’s not inevitable, but it underscores the need to fund and monitor proactively.
Who is Universal Life Insurance Best Suited For?
UL can be a smart fit for Illinois residents who:
- Have high or variable income and want flexibility
- Have maxed out qualified retirement accounts and want additional tax-deferred accumulation
- Want lifelong coverage for estate planning or business continuity
- Value the ability to adjust premiums and death benefit over time
- Are willing to review and maintain the policy periodically
Cost example to set expectations: For a $250,000 UL policy, a healthy, non-smoking 40-year-old male might see averages around $103–$150 per month, and a similarly healthy female around $83–$130 per month. Your actual pricing in Illinois will vary by age, health, and policy design. For current examples and guidance, visit our Illinois-focused breakdown: Average cost of a $250,000 policy.
Is Universal Life Insurance Considered a Good Investment Strategy?
Short answer: UL is primarily life insurance with a savings component—not a replacement for 401(k)s or IRAs.
- Where UL can shine: As a supplemental tool after maxing tax-advantaged retirement accounts or when you value permanent coverage plus optional access to cash value.
- Fees vs. returns: Policy costs reduce net growth, and returns are not guaranteed in IUL/VUL.
- Use-case: Think of UL as an options-creator—flexible coverage first, supplemental accumulation second.
If you’re leaning toward IUL for upside potential with floor protection, see how indexing and caps work in How Cash Value Works in Indexed Universal Life.
What Happens if the Cash Value in a Universal Life Policy Becomes Depleted?
If cash value is too low to cover monthly COI and fees:
- The policy enters a grace period. You’ll get a notice with the amount needed to keep it in force.
- If you don’t pay the required amount by the deadline, the policy lapses—coverage ends.
- Reinstatement may be possible within a set period, subject to underwriting and back premiums plus interest.
- Outstanding loans can accelerate lapse if interest accrues and outpaces growth.
Common causes of depletion:
- Consistently paying only the minimum when COI rises with age
- Prolonged low crediting rates or market underperformance
- Large withdrawals or accumulating loan balances
Pro tip: Set annual reminders to review funding, COI, and projected performance. Slight overfunding early can dramatically improve durability later.
Frequently Asked Questions about How Universal Life Insurance Works
Are there any tax implications associated with universal life insurance?
- Death benefit: Generally income-tax free to beneficiaries.
- Cash value: Grows tax-deferred.
- Withdrawals: Taxed on a FIFO basis for non-MEC policies—your basis (premiums paid) comes out first, then gains are taxable as ordinary income.
- Loans: Generally not taxable if the policy stays in force and isn’t a MEC; unpaid loans reduce the death benefit.
- MEC status: If a policy becomes a Modified Endowment Contract, loans and withdrawals are taxed as gain-first and may face a 10% penalty before age 59½.
For Illinois-specific consumer guidance, the state regulator’s page is a helpful reference: Buying Life Insurance – Illinois Department of Insurance. This is general information, not tax advice—always consult your tax professional.
What happens to the cash value when the policyholder dies?
In most UL policies, beneficiaries receive the death benefit, and the insurer retains the cash value. If you select Option B (Increasing Death Benefit), beneficiaries receive the base amount plus the cash value. Because design choices matter a lot here, we’ll help you compare options side-by-side.
How much does universal life insurance cost?
Pricing depends on your age, health, tobacco use, policy type, and rider choices. As a directional reference, a healthy 40-year-old in Illinois might see:
- Male: roughly $103–$150 per month for $250,000 in coverage
- Female: roughly $83–$130 per month for $250,000 in coverage
See current examples and request quotes here: Average cost of a $250,000 policy. We’ll not only show options—you’ll see how design choices affect durability and long-term costs.
How to Set Up and Maintain a Healthy Universal Life Policy
Because we’re often asked for a practical “how-to,” here’s our simple playbook:
-
Define your goal
- Pure lifetime protection at the best price? Consider GUL.
- Flexibility with growth potential? Consider traditional UL or IUL.
- Comfortable with market risk? Consider VUL.
-
Choose your death benefit option
- Option A (Level) for lower cost today
- Option B (Increasing) to preserve cash value for heirs
-
Fund smartly
- Aim for at least the target premium to build a cushion.
- Overfund early if possible—compounding and COI trends reward early funding.
-
Add riders selectively
- No-lapse guarantee for added protection against lapse
- Accelerated death benefits for chronic or terminal illness
- Waiver of premium for disability
-
Monitor annually
- Review cash value, COI, and crediting performance
- Adjust premiums as life changes—raise during strong income years, dial back during lean ones
-
Protect against insurer risk
- Work with strong carriers—verify ratings via AM Best
-
Borrow and withdraw wisely
- Prefer policy loans over withdrawals when appropriate to preserve basis
- Track loan interest and avoid overborrowing
- Keep an emergency funding plan to prevent lapse if markets dip
-
Get help when needed
- We’ll model multiple scenarios for Illinois policies so you can see the long-term impact of funding levels, loans, and death benefit options.
Bonus: Indexed UL Deep-Dive
Considering an IUL? These are the key levers:
- Participation rate: Example, 80% participation means you earn 80% of an index’s gain.
- Cap: The maximum annual credit, say 10%.
- Floor: The minimum, often 0%, so negative years don’t reduce credited interest.
- Fees and policy charges still apply, so net growth can differ from headline index returns.
If you want the 101 and the math, we made it simple here: How Does IUL Work and What is IUL.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Paying only the minimum premium for years—then getting blindsided as COI rises with age.
- Ignoring annual statements and not adjusting contributions when performance lags.
- Treating UL as your primary investment vehicle instead of a supplemental one.
- Taking large withdrawals that trigger taxes or deplete the policy’s cushion.
- Letting loan interest snowball until the policy collapses.
We’ll help you stress test your policy so your long-term plan doesn’t hinge on rosy assumptions.
Where ShieldWise Fits In
We’re a digital insurance marketplace based in Illinois focused on life insurance, indexed universal life, final expense, and Medicare coverage. You can compare plans from trusted carriers, get instant online quotes, and receive clear, jargon-free guidance. Our specialty is translating all the moving parts—COI, caps, floors, MEC limits—into plain English so you can act with confidence.
Helpful next reads from us:
- Universal Life Insurance Guide 2026
- Universal Life Cash Value and Flexibility
- How Cash Value Works in Indexed Universal Life
- Universal Life Term Versus Permanent
- How IUL Loans Work
- What is IUL
- What Is Universal Life (UL) Insurance?
Take Control of Your Financial Future
Universal life insurance offers unparalleled flexibility for lifelong protection and wealth building, but it requires understanding. By balancing the cost of insurance with cash value growth, you can create a policy that adapts to your life’s changes. To explore if a universal life policy is the right fit for your strategy, compare your options. ShieldWise can help you steer the complexities and find the right plan. Explore your universal life insurance options today.
Appendix: Quick Reference
Because we’re all about making complex things simple, here’s a fast recap of the most-searched items tied to “how does universal life insurance work”:
- UL basics: Permanent coverage + cash value + flexible premiums
- Premium anatomy: COI + policy fees + cash value contribution
- Cash value growth: Fixed, indexed, or market-based—tax-deferred
- Options A vs. B: Level vs. Increasing death benefit
- Accessing cash: Loans usually tax-free while in force; withdrawals may be taxable
- Lapse risk: Monitor funding; COI rises with age; don’t let cash value hit zero
- MEC watch: Overfunding too aggressively can change tax treatment
- Insurer strength matters: Check AM Best
- Illinois consumers: Start with the state’s guide if you’re new to life insurance shopping—Illinois Department of Insurance
And yes, we’ll happily walk you through a side-by-side of UL, IUL, VUL, GUL, and term so you can see—at a glance—what’s worth paying for and why.
Additional Visuals Used in This Guide
- A visual guide to how universal life insurance works.
- An infographic detailing the division of a universal life insurance premium.
- A diagram illustrating the flow of premiums into the cost of insurance and cash value.
- A conceptual image of a branching tree representing the different types of universal life insurance.
If you’re ready to see real numbers for your situation, we’re ready to help—without the jargon and without the pressure.

