Why Understanding Medicare Supplement and Medigap Matters for Your Retirement
Medicare Supplement and Medigap are two names for the same private insurance that helps pay for costs Original Medicare doesn’t cover. If you have Original Medicare (Parts A and B), you face deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments that can add up. Medigap policies fill these financial gaps.
Quick Answer: What is Medicare Supplement Insurance (Medigap)?
- What it is: Extra insurance you buy from a private company to cover out-of-pocket costs in Original Medicare
- What you need: Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance) and Part B (Medical Insurance)
- What it covers: Copayments, coinsurance, deductibles, and sometimes foreign travel emergencies
- What it doesn’t cover: Prescription drugs, long-term care, dental, vision, or hearing aids
- Key fact: All plans with the same letter (like Plan G) offer the same benefits—only the price differs between insurance companies
For example, in 2025, you face a $1,676 Part A deductible per benefit period and a $257 Part B deductible. A hospital stay for days 61-90 costs $419 per day in coinsurance. Without Medigap, these costs are your responsibility.
Original Medicare covers about 80% of your healthcare costs after you meet your deductibles. The remaining 20% is unpredictable and can be expensive, especially during a serious illness.
Medigap provides financial predictability. You pay a monthly premium, and in return, surprise bills are mostly eliminated. You can see any doctor who accepts Medicare without network restrictions or referrals.
There are 10 standardized Medigap plans (A through N), each offering a different level of coverage. The best time to buy is during your 6-month Medigap Open Enrollment Period, which starts when you’re 65+ and enrolled in Part B. During this time, insurers cannot deny you coverage or charge more based on your health.
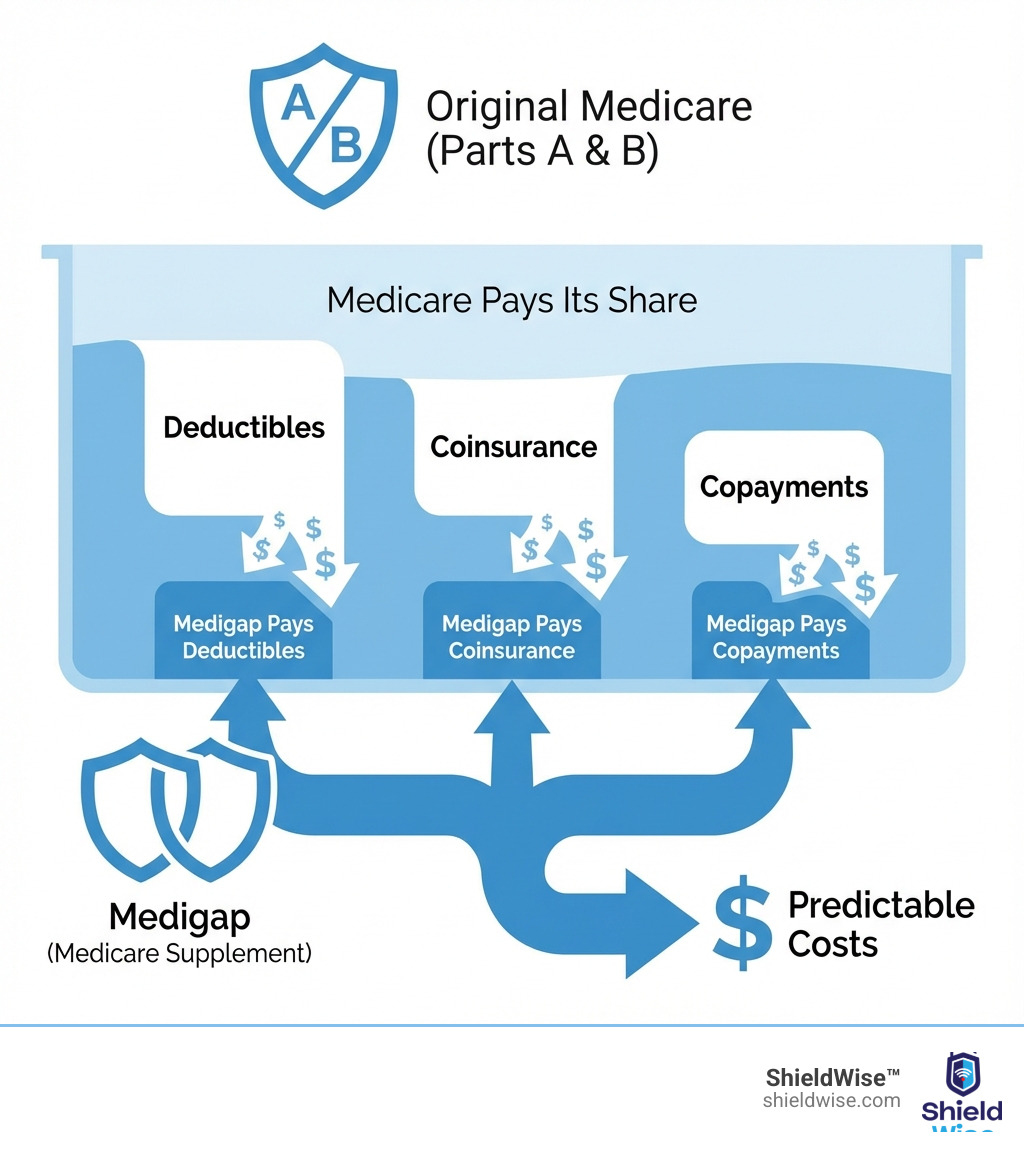
What is Medigap and How Does It Work with Original Medicare?
Medigap acts as a financial safety net for Original Medicare (Parts A and B), which leaves “gaps” like deductibles and coinsurance. These Medicare – supplement and medigap policies cover many of those out-of-pocket costs, making your healthcare expenses more predictable.
To be eligible, you must have Medicare Parts A and B. Medigap works with Original Medicare, not as a replacement. After Medicare pays its share for a service, your Medigap policy pays its portion as a secondary payer.
A key benefit is freedom of choice: you can see any doctor or hospital in the U.S. that accepts Medicare, with no network restrictions or referrals needed. This control, combined with predictable costs, helps you avoid large, unexpected medical bills.

What Medigap Policies Cover
Medigap policies are standardized, meaning a Plan G from one company offers the same basic benefits as a Plan G from another. This makes it easier to compare plans based on price. Here’s what various Medicare – supplement and medigap plans can cover:
- Medicare Part A Coinsurance and Hospital Costs: Covers your share of hospital costs, including up to 365 extra days after Medicare benefits end. This helps with expenses like the 2025 daily coinsurance of $419 for hospital days 61-90.
- Medicare Part B Coinsurance or Copayment: Most plans cover the 20% coinsurance for Part B services that you’re typically responsible for after meeting your deductible.
- Blood (First 3 Pints): Covers the cost of the first three pints of blood annually.
- Part A Hospice Care Coinsurance or Copayment: Covers your share of hospice care costs.
- Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) Care Coinsurance: Covers your coinsurance for skilled nursing facility care after a hospital stay.
- Part A Deductible: Many plans cover the Part A deductible, which is $1,676 per benefit period in 2025.
- Part B Deductible: The annual Part B deductible ($257 in 2025). Note: Plans C and F, which covered this, are unavailable to new enrollees since 2020.
- Part B Excess Charges: Plans F and G cover excess charges, which are up to 15% above the Medicare-approved amount that some doctors may charge.
- Foreign Travel Emergency: Some plans cover 80% of approved costs for medical emergencies outside the U.S., after a deductible and up to plan limits.
What Medigap Policies Do NOT Cover
It’s crucial to know what Medicare – supplement and medigap policies do not cover. These policies supplement Original Medicare and do not provide comprehensive, all-in-one benefits.
Generally, Medigap policies do NOT cover:
- Long-Term Care (like nursing home or custodial care)
- Vision Care (routine exams, glasses)
- Dental Care (routine check-ups, fillings)
- Hearing Aids
- Eyeglasses
- Private-Duty Nursing
- Prescription Drugs (Part D): You’ll need a separate Medicare Part D plan for prescription drug coverage.
Medigap policies only cover costs for services that Original Medicare covers. If Medicare doesn’t cover a service, your Medigap policy won’t either.
Understanding Your Options for Medicare – Supplement and Medigap Plans
Standardization is key to understanding Medicare – supplement and medigap plans. In most states, including Illinois, policies are identified by letters A through N. A Plan G from one company has the same core benefits as a Plan G from another; only the price differs. This simplifies shopping: choose the plan letter that fits your needs, then compare prices from different insurers. (Note: Massachusetts, Minnesota, and Wisconsin have their own standardized plans.)
For a comprehensive guide, consult official resources like the Choosing A Medigap Policy: A Guide To Health Insurance For People With Medicare.
Here’s a table summarizing the basic benefits of the standardized Medigap plans:
| Basic Benefits | Plan A | Plan B | Plan C | Plan D | Plan F | Plan G | Plan K | Plan L | Plan M | Plan N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part A Coinsurance & Hospital Costs (up to 365 extra days) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Part B Coinsurance or Copayment | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 50% | 75% | ✔ | ✔* |
| Blood (First 3 Pints) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 50% | 75% | ✔ | ✔ |
| Part A Hospice Care Coinsurance or Copayment | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 50% | 75% | ✔ | ✔ |
| Skilled Nursing Facility Care Coinsurance | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 50% | 75% | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Part A Deductible | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 50% | 75% | ✔ | ✔ | |
| Part B Deductible | ✔ | ✔ | ||||||||
| Part B Excess Charges | ✔ | ✔ | ||||||||
| Foreign Travel Emergency (80% up to plan limits) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Out-of-Pocket Limit | $7,220 | $3,610 |
*Plan N pays 100% of the Part B coinsurance, except for a copayment of up to $20 for some office visits and up to $50 for emergency room visits that don’t result in inpatient admission.
*Plans C and F are not available to people new to Medicare on or after January 1, 2020.
The End of Plans C & F for New Enrollees
Due to a 2020 law change (MACRA), Medigap Plans C and F, which cover the Part B deductible, are no longer available to people new to Medicare. If you were eligible for Medicare before January 1, 2020, you can still buy or keep these plans. For everyone else, these comprehensive options are off the table, making alternatives like Plan G more important than ever. For more details, refer to the official Compare Medigap Plan Benefits page.
Plan G: The New Standard for Comprehensive Coverage
With Plans C and F unavailable to new enrollees, Plan G is now the most comprehensive and popular option. It covers everything Plan F did, except for the annual Medicare Part B deductible ($257 in 2025). Once you pay that deductible, Plan G covers 100% of your remaining approved costs, including Part B coinsurance and excess charges. For many, paying the small annual deductible is a worthwhile trade-off for extensive coverage.
A High-Deductible Plan G is also available in some states. It offers lower premiums but requires you to pay all Medicare-covered costs up to a higher deductible ($2,870 in 2025) before the plan pays. This is a good choice for those who want catastrophic coverage with lower monthly payments.
Understanding Cost-Sharing Plans: K, L, M, and N
Plans K, L, M, and N are cost-sharing Medicare – supplement and medigap options with lower monthly premiums. In exchange, you pay a portion of your medical costs through coinsurance or copayments.
- Plans K and L: These plans cover a percentage of certain benefits (50% for K, 75% for L) until you reach an annual out-of-pocket limit ($7,220 for K, $3,610 for L in 2025). After reaching the limit, the plan pays 100% for the rest of the year. They offer a safety net for those comfortable with some cost-sharing for a lower premium.
- Plan M: This plan is similar to Plan D but covers only 50% of the Part A deductible, lowering the premium.
- Plan N: A popular choice, Plan N balances lower premiums with strong coverage. It covers 100% of Part B coinsurance but requires small copayments for some office visits (up to $20) and ER visits (up to $50). It doesn’t cover the Part B deductible or excess charges. The lower premium often makes these predictable copays an attractive trade-off.
Navigating Medigap Costs and Enrollment
Understanding when and how to enroll in a Medicare – supplement and medigap policy is just as important as knowing what it covers. The timing of your enrollment can significantly impact your access to coverage and the premiums you pay.

The best time to buy a Medigap policy is during your one-time, six-month Medigap Open Enrollment Period. It starts the month you’re 65 or older and enrolled in Medicare Part B. During this window, insurance companies cannot deny you coverage or charge more based on your health. You are guaranteed acceptance at the best rates.
If you miss this period, insurers in Illinois and most states can use medical underwriting, which may lead to denial or higher premiums based on your health history. It’s a critical “use it or lose it” opportunity.
You may also have guaranteed issue rights to buy a policy outside of open enrollment without medical underwriting. These rights apply in specific situations, like losing other health coverage. Examples include your Medicare Advantage plan ending its service in your area, losing employer group coverage, or trying a Medicare Advantage plan for the first time and switching back to Original Medicare within a year.
For more information on navigating your initial enrollment, check out our guide on Medicare Basics: Turning 65.
Decoding the Costs of Medicare – Supplement and Medigap Policies
Your primary cost for a Medicare – supplement and medigap policy is the monthly premium paid to the private insurer, in addition to your regular Part B premium. Medigap premiums vary based on the plan, company, age, and location. These premiums cover significant out-of-pocket costs from Original Medicare, such as:
- Part A Deductible: $1,676 per benefit period (2025)
- Part A Coinsurance: $419 per day for hospital stays (days 61-90 in 2025)
- Part B Deductible: $257 annually (2025), which you pay with most plans
Choosing a plan involves a trade-off. A comprehensive plan like G has a higher premium but fewer out-of-pocket costs than a cost-sharing plan like N.
How Medigap Premiums Are Priced
Understanding how insurers price Medicare – supplement and medigap premiums is key to managing long-term costs. There are three methods:
- Community-Rated: Everyone in a given area pays the same premium, regardless of age. Premiums don’t increase as you get older, only for inflation.
- Issue-Age-Rated: The premium is based on your age when you buy the policy. It won’t increase due to your age but can rise with inflation.
- Attained-Age-Rated: The premium is based on your current age and increases as you get older. These policies start cheaper but can become expensive over time.
In Illinois, companies can use any method. Always ask which one is used, as it significantly impacts your future costs. For a deeper dive into guaranteed issue rights, refer to the official guide on Guaranteed issue rights explained.
Choosing Your Path: Medigap vs. Medicare Advantage
When you enroll in Medicare, you face a key choice: Original Medicare with a Medicare – supplement and medigap policy, or a Medicare Advantage (Part C) plan. You cannot have both.
Original Medicare + Medigap: This path offers maximum flexibility. You can see any doctor nationwide who accepts Medicare, without referrals. You pay a monthly Medigap premium for highly predictable out-of-pocket costs.
Medicare Advantage (Part C): These are all-in-one plans from private insurers that replace Original Medicare. They often bundle prescription drug (Part D), dental, and vision coverage. They typically have low or $0 premiums but use provider networks (HMOs/PPOs) and require copayments for services.
The decision is a trade-off between monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs, and between provider freedom and bundled benefits.
Key Differences in Your Medicare – Supplement and Medigap Choice
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences to help you decide:
- Provider Networks:
- Medigap: Freedom to see any provider nationwide that accepts Medicare, with no referrals.
- Medicare Advantage: Plans use networks (HMOs or PPOs). You may need referrals, and out-of-network care costs more.
- Cost Structure:
- Medigap: Higher monthly premium for minimal, predictable out-of-pocket costs for services.
- Medicare Advantage: Low or $0 monthly premium but you pay copayments for services until you reach an annual out-of-pocket maximum.
- Prescription Drug Coverage:
- Medigap: Requires purchasing a separate Medicare Part D plan for drug coverage.
- Medicare Advantage: Most plans (called MAPDs) include prescription drug coverage.
- Extra Benefits:
- Medigap: Does not include extra benefits like dental, vision, or hearing.
- Medicare Advantage: Often includes extra benefits like routine dental, vision, hearing, and gym memberships.
- Travel Coverage:
- Medigap: Some plans (C, D, F, G, M, N) cover foreign travel emergencies.
- Medicare Advantage: International travel coverage is limited and varies by plan.
Your choice depends on your priorities. If you prioritize provider freedom and predictable costs, Medigap is a strong choice. If you prefer lower premiums and bundled benefits and are comfortable with networks, consider Medicare Advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions about Medigap
Here are answers to common questions about Medicare – supplement and medigap options.
Can my Medigap insurance company drop me?
Generally, no. Your Medigap policy is guaranteed renewable, meaning the insurer cannot cancel it as long as you pay your premiums. Your benefits cannot be changed. The only exceptions are if you stop paying, provided false information on your application, or the insurance company goes bankrupt.
Do I need a separate Medigap policy for my spouse?
Yes. Medigap policies are individual, not family plans. You and your spouse must each buy a separate policy, even if you choose the same plan.
What is a Medicare SELECT policy?
A Medicare SELECT policy is a type of Medicare – supplement and medigap plan that requires you to use providers in a specific network for full benefits, though emergency care is covered out-of-network. In exchange for this restriction, SELECT plans usually have lower premiums. If you buy a SELECT plan, you generally have a 12-month right to switch to a standard Medigap policy from the same insurer if you’re not satisfied with the network.
Conclusion: Securing Your Financial Health with the Right Coverage
Understanding Medicare – supplement and medigap policies is a crucial step toward financial health in retirement. These plans solve the problem of “gaps” in Original Medicare by converting unpredictable costs into a manageable monthly premium.
By choosing a Medigap policy, you gain:
- Financial Predictability: Most of your cost-sharing is covered, eliminating surprise bills.
- Freedom of Choice: See any doctor or hospital that accepts Medicare, nationwide, without referrals.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Plans like G protect you against major medical expenses.
The key is to compare options based on your health needs and budget, especially during your Medigap Open Enrollment Period.
At ShieldWise™, we provide clear guidance for your Medicare options in Illinois. Our digital marketplace lets you compare plans from trusted carriers, get instant quotes, and secure the right coverage easily. We’re here to help you make an informed decision for your peace of mind in retirement.
