Understanding the Basics: What is Indexed Universal Life Insurance?
Indexed Universal Life (IUL) insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that combines a death benefit with a cash value component that can grow based on the performance of a stock market index, like the S&P 500. Understanding IUL – basics and education starts with this core concept.
Here’s what you need to know about IUL basics:
- Permanent Coverage: Unlike term life insurance, IUL lasts your entire life as long as premiums are paid
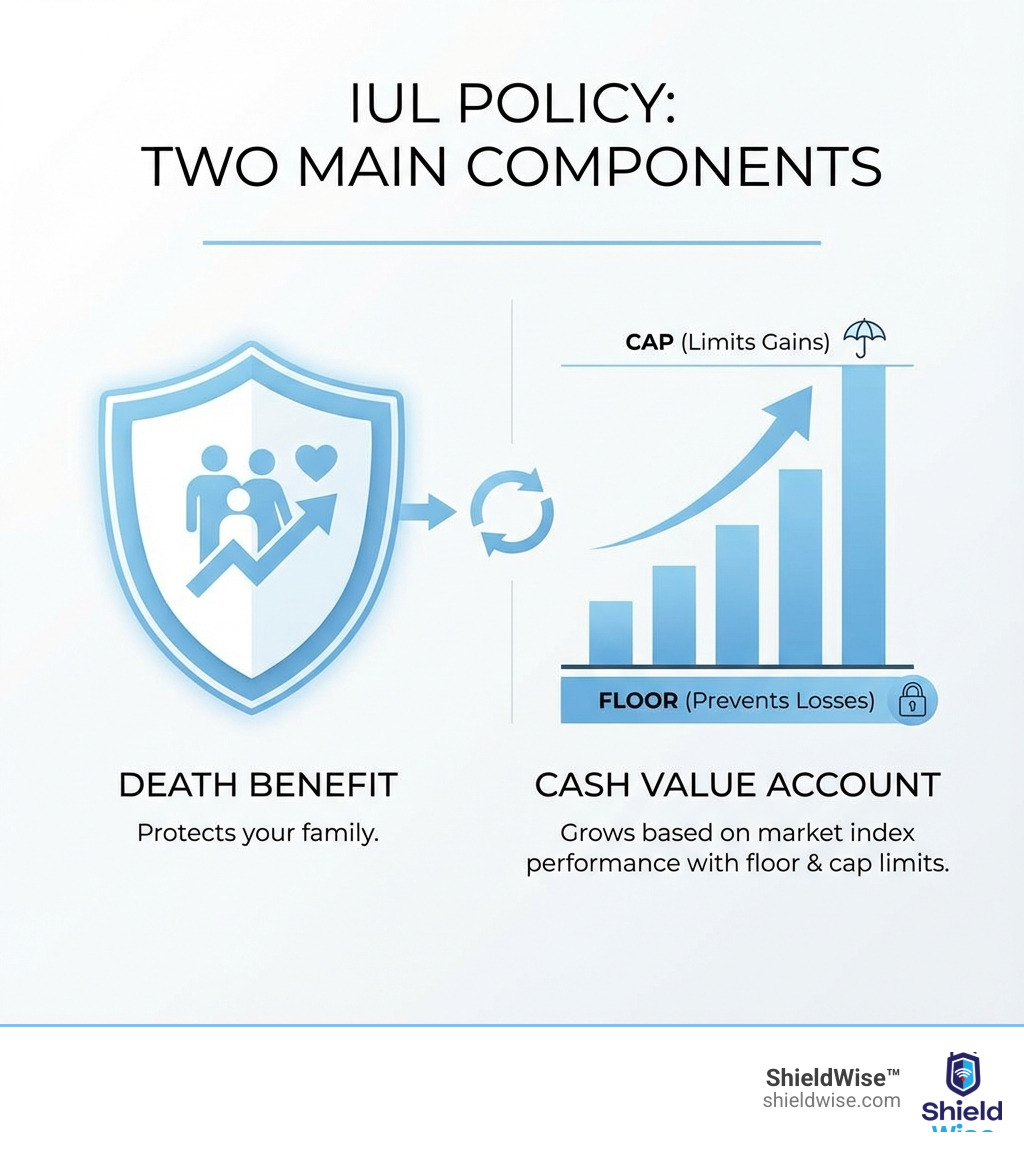
- Two Main Parts: A guaranteed death benefit for your family and a cash value account that grows over time
- Market-Linked Growth: Your cash value earns interest based on how well a market index performs
- Built-In Protection: A “floor” (typically 0%) means you won’t lose money when the market drops
- Growth Limits: A “cap” (often 7-12%) limits how much you can earn when the market goes up
- Flexible Premiums: You can adjust how much you pay within certain limits
- Tax Advantages: Cash value grows tax-deferred, and loans are generally tax-free
If you’re on a fixed income or want straightforward protection, IUL might be more complex than you need. But if you want to understand how permanent life insurance can work as both protection and a financial tool, this guide will explain it in plain English.
Financial educators describe IUL as “life insurance with no term limit, plus ancillary benefits.” The strategy involves building cash value you can borrow against, creating an “additional funding source” for the future.
The catch? IUL is complicated. It requires understanding caps, floors, participation rates, and fees. Many have heard stories about policies that didn’t perform as expected or agents who designed policies that benefited themselves more than the policyholder.
That’s exactly why clear, honest education matters.
In this guide, we’ll break down how IUL works, who it’s for, what it costs, and how it compares to simpler options. By the end, you’ll know if IUL deserves a place in your financial plan.
How an IUL Policy Works: The Core Mechanics
So, how does this financial tool actually work? An IUL policy blends the stability of life insurance with the growth potential of market indexes. Let’s explore the core mechanics.

When you pay an IUL premium, a portion covers the cost of insurance and administrative fees. The rest is added to your policy’s cash value. This is where the complexity of IUL – basics and education begins.
Cash Value Accumulation and Index Crediting
The cash value in an IUL policy can grow on a tax-deferred basis, linked to the performance of a stock market index like the S&P 500. Your cash value isn’t directly invested in the stock market. Instead, the insurance company uses financial instruments, often options, to credit interest based on the index’s performance. This indirect link is key to the policy’s unique risk-reward profile.
Here’s how index crediting typically works:
- Caps: The maximum interest rate your cash value can earn in a given period. For example, if the index gains 15% but your policy has a 10% cap, your cash value is credited with 10%. Caps typically range from 8% to 12%.
- Floors: Your downside protection, often set at 0%. This guarantees your cash value won’t lose money from negative market performance. If the index drops by 5%, your cash value is credited with 0% interest, preserving your principal.
- Participation Rates: Determines what percentage of the index’s gains are credited to your cash value, up to the cap. For instance, with an 80% participation rate, a 10% index gain would result in an 8% credit (assuming it’s below the cap). These rates can sometimes be changed by the insurer.
The actual calculation of these gains can vary depending on the crediting method (e.g., Daily Average, Annual Point-to-Point), which can impact how market fluctuations affect your cash value.
Flexible Premiums and Death Benefits
A defining feature of IUL is flexibility. You can adjust your premium payments within certain limits, paying more to accelerate cash value growth or less in a pinch, as long as your cash value covers policy costs. Similarly, the death benefit can often be adjusted, though increasing it typically requires further underwriting.
This flexibility, combined with tax-deferred cash value growth, makes IUL a dynamic financial tool. However, it also introduces complexity that requires careful monitoring.
For a deeper dive into the inner workings, you can find More info about how IUL works.
The Pros and Cons of Indexed Universal Life Insurance
Like any sophisticated financial product, IUL has advantages and disadvantages. Understanding both sides is crucial for a well-rounded IUL – basics and education.

Key Benefits of an IUL Policy
Many are drawn to IUL for its unique blend of protection and potential growth. Here’s why:
- Potential for Higher Returns: Compared to whole life, IUL offers potentially higher cash value returns because its growth is linked to stock market indexes. While whole life provides guaranteed growth, IUL aims for more upside.
- Downside Protection: A key advantage is the “floor” (typically 0%), which guarantees your cash value won’t decrease due to market downturns. This principal protection offers security against market volatility.
- Tax Advantages:
- Tax-Deferred Cash Value Growth: Your cash value accumulates interest without being taxed annually.
- Tax-Free Death Benefit: The death benefit paid to your beneficiaries is generally income tax-free.
- Tax-Free Policy Loans: You can typically access your cash value through policy loans, which are generally tax-free if the policy remains in force.
- Flexibility: IUL policies offer significant flexibility. You can adjust premium payments within certain limits and often adjust your death benefit to match evolving needs.
- Estate Planning Tool: The tax-free death benefit makes IUL an effective tool for passing wealth to heirs efficiently.
- Diversification: IUL can serve as a diversification tool within a broader portfolio, offering a different growth mechanism than direct stock investments.
Potential Risks and Drawbacks to Consider
While the benefits are appealing, it’s important to be aware of the potential downsides:
- Caps on Returns: The flip side of downside protection is a cap on returns. If the market soars 15% but your policy’s cap is 10%, your gain is limited to 10%.
- Complexity: IUL policies are notoriously complex, requiring an understanding of caps, floors, participation rates, and fees. This can be a drawback for those who prefer simpler products.
- Policy Illustrations are Not Guarantees: Policy illustrations project potential growth but are not guarantees. If the policy underperforms, you might need to pay higher premiums to keep it in force.
- Management Fees and Costs: IUL policies have various fees (cost of insurance, administrative, surrender charges) that can erode your cash value, especially in the early years or during low index performance.
- Risk of Policy Lapse: If cash value growth is insufficient to cover policy costs, the policy can lapse. This ends your coverage and could create tax consequences for any gains you’ve borrowed.
- Growth Does Not Include Stock Dividends: IUL policies typically do not credit cash value with stock dividends, which are a significant component of overall stock market returns.
- Less Optimal for Primary Retirement Savings: For most people, traditional retirement vehicles like a 401(k) or IRA are better primary savings vehicles due to lower fees and no earnings caps. IUL is often best as a supplemental strategy.
Navigating these pros and cons requires careful consideration of your financial goals and risk tolerance.
IUL Compared to Other Life Insurance Options
To truly grasp the value proposition of IUL, it’s helpful to see how it stacks up against other popular life insurance products. This comparison is a cornerstone of IUL – basics and education.
Life insurance generally falls into two broad categories: term and permanent. IUL is a type of permanent life insurance, but even within that category, it has distinct characteristics.
IUL vs. Term Life Insurance
- Cost: Term life insurance is the most affordable option, providing coverage for a specific period (e.g., 10-30 years). IUL is more expensive because it offers lifelong coverage and a cash value component.
- Coverage Duration: Term life is temporary; IUL is permanent, providing coverage for your entire life as long as premiums are paid.
- Cash Value: Term life has no cash value component. IUL builds cash value that can grow and be accessed.
- Growth Potential: Term life offers no growth. IUL offers market-linked growth potential for its cash value.
- Flexibility: Term life is fixed. IUL offers flexible premiums and death benefits.
IUL vs. Whole Life Insurance
Both IUL and whole life are permanent policies with cash value, but their mechanics differ significantly:
- Cost: IUL can be less expensive than whole life but has greater risk and complexity. Whole life has higher, fixed premiums.
- Cash Value Growth:
- Whole Life: Cash value grows at a guaranteed rate, making it predictable and stable. It also often pays dividends, though these are not guaranteed.
- IUL: Cash value growth is linked to a market index, offering potential for higher returns, but with caps and participation rates. It typically does not pay dividends.
- Flexibility:
- Whole Life: Premiums are fixed and guaranteed. The death benefit is also guaranteed.
- IUL: Offers flexible premiums and potentially a flexible death benefit, allowing adjustments based on your financial situation.
- Risk: Whole life is less risky due to its guaranteed growth and fixed premiums. IUL carries more risk because its growth is tied to index performance, albeit with a floor.
- Complexity: Whole life is more straightforward. IUL is more complex due to its indexing methods, caps, floors, and variable performance.
IUL vs. Variable Universal Life (VUL) Insurance
VUL is another type of permanent life insurance with investment potential, but it takes a different approach:
- Investment Risk:
- IUL: Less risky than VUL because your cash value isn’t directly invested in the stock market. It’s linked to an index and typically has a 0% floor to protect against losses.
- VUL: Policyholders can directly invest their cash value in subaccounts, similar to mutual funds. This offers unlimited growth potential but also carries the full risk of market losses, meaning you can lose principal.
- Complexity: Both are complex, but VUL requires more hands-on management and a higher risk tolerance due to direct market exposure.
Here’s a quick comparison table to summarize:
| Feature | Term Life Insurance | Whole Life Insurance | Indexed Universal Life (IUL) | Variable Universal Life (VUL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lowest | Higher | Moderate to High | Moderate to High |
| Coverage Duration | Temporary (e.g., 20 years) | Permanent | Permanent | Permanent |
| Cash Value | None | Guaranteed, fixed growth | Market-linked (caps/floors) | Market-invested (full market risk) |
| Growth Potential | None | Moderate, guaranteed | Moderate to High, capped | High, but with full market risk |
| Flexibility | Low | Low (fixed premiums) | High (flexible premiums/DB) | High (flexible premiums/DB/investments) |
Understanding these distinctions is essential when considering which type of life insurance best aligns with your financial objectives. For more on Universal Life options, including IUL, you can explore More info about Universal Life Insurance.
Advanced IUL – Basics and Education for Your Financial Strategy
Now that we’ve covered the fundamentals, let’s explore who IUL is best suited for, its costs, and how to access its cash value—all advanced topics in IUL – basics and education.
Is an IUL Right for You? Key IUL – Basics and Education Considerations
IUL isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s particularly well-suited for certain financial profiles and goals. Consider if you fit these categories:
- High-Net-Worth Individuals: IULs are attractive for lowering taxable income or for sophisticated estate planning. The tax-free death benefit and tax-deferred growth are valuable for wealth transfer.
- Maxed-Out Retirement Accounts: If you’ve maxed out your 401(k) and IRA contributions, an IUL can serve as a supplemental savings vehicle with additional tax-deferred growth potential.
- Long-Term Financial Goals: IUL is a long-term strategy for individuals committed to keeping the policy in force for many years to allow significant cash value accumulation.
- Supplemental Retirement Income: The ability to take tax-free loans from cash value can provide a flexible, tax-diversified source of supplemental retirement income.
- Business Succession Planning: Business owners can use IUL for key person insurance or as part of a premium-financing plan to provide business liquidity and protection.
- Risk Tolerance: IUL has downside protection but still involves market-linked risk. It’s best for those comfortable with this nuanced risk profile who are willing to monitor their policy.
For most people, a 401(k) is a better primary retirement vehicle due to lower fees and no earnings cap. IUL is life insurance first, with cash value growth as a secondary benefit.
Understanding IUL Costs and the 7-Pay Rule
IUL costs are a critical part of IUL – basics and education. They offer benefits but come at a higher price than term life insurance.
Cost Factors: Your IUL policy cost will be influenced by:
- Age: Younger individuals generally pay lower premiums.
- Health: Excellent health ratings lead to lower costs.
- Gender: Historically, women tend to pay less for life insurance than men.
- Coverage Amount: A higher death benefit results in higher premiums.
- Riders: Additional options will add to the cost.
Typical Costs: Beyond premiums, you’ll encounter fees like:
- Cost of Insurance (COI): Covers mortality charges for your death benefit.
- Administrative Fees: Charges for managing the policy.
- Surrender Charges: Fees for canceling the policy early (often in the first 10-15 years).
- Management Fees: Fees for the indexed accounts.
For example, average annual premiums for a $500,000 IUL policy for a healthy, non-smoking man can range from around $2,584 at age 20 to $18,309 at age 60. These costs can rise if cash value growth doesn’t cover them.
The 7-Pay Rule
The 7-pay rule is a crucial federal tax test for life insurance. It limits the premiums you can pay into a policy during its first seven years. If you exceed this limit, the policy becomes a Modified Endowment Contract (MEC).
What happens if your IUL becomes a MEC?
- Death Benefit: Remains tax-free.
- Cash Value Growth: Still grows tax-deferred.
- Distributions: This is the key difference. Loans and withdrawals are taxed as “income first” (LIFO). Distributions before age 59½ may also be subject to a 10% federal penalty tax.
Adhering to the 7-pay rule is vital for maintaining the most favorable tax treatment of your IUL’s cash value.
Accessing Your Cash Value and Finding Reliable IUL – Basics and Education
Accessing your IUL’s cash value is an attractive feature, but it’s important to understand the implications.
How to Access Your Cash Value
You have two primary ways to access the cash value:
- Policy Loans: You can borrow against your cash value, and these loans are generally tax-free as long as the policy is active. You’ll pay interest, but repayment can be flexible. An unpaid loan reduces the death benefit and could become taxable if the policy lapses.
- Withdrawals: You can withdraw from your cash value, which reduces both your cash value and death benefit. Withdrawals are tax-free up to your cost basis (the premiums you’ve paid). Amounts withdrawn above your cost basis are taxable gains.
Accessing funds can involve fees and surrender charges, especially in early years. Significant cash value accumulation typically takes several years.
Finding Reliable Educational Resources and Professional Advice
Given IUL’s complexity, seeking reliable IUL – basics and education is paramount. Here’s where to find trustworthy guidance:
- Licensed Insurance Agents and Financial Advisors: These professionals can explain IUL nuances, tailor a policy to your needs, and review illustrations. Look for agents with designations like Chartered Life Underwriter (CLU) or those who act as fiduciaries.
- Fiduciary Advisors: A fiduciary is legally bound to act in your best interest. This is a critical distinction with complex products where commissions can influence recommendations. We recommend working with fiduciaries for significant financial decisions. You can learn more about Working with fiduciaries.
- Insurance Company Resources: Reputable insurance companies offer educational materials, white papers, and webinars on IUL products.
- Independent Financial Education Platforms: Websites specializing in financial education can offer unbiased explanations and comparisons.
Always review policy details and consult a professional to understand an IUL’s benefits, limits, and costs for your specific situation.
Frequently Asked Questions about IUL Insurance
Even after a deep dive, some questions inevitably linger. Let’s tackle some of the most common FAQs surrounding IUL – basics and education.
Can you lose money in an IUL policy?
The answer is nuanced. You are unlikely to lose your principal in an IUL policy from negative market performance, thanks to the 0% floor guarantee. This means if the linked index drops, your cash value is typically credited with 0% interest, protecting your principal from market downturns.
However, your cash value can decrease if the fees and cost of insurance outweigh the interest credited from the index. If the market performs poorly for an extended period and your cash value is consistently credited with 0% interest, the ongoing costs could erode your cash value. This is why careful monitoring and understanding your policy’s expenses are crucial.
How soon can you borrow from an IUL?
You can typically borrow from your IUL policy once sufficient cash value has accumulated. This usually takes a few years, depending on how much you pay in premiums and the specific structure of your policy.
In the initial years, a significant portion of your premiums goes towards covering insurance costs and administrative fees, and surrender charges are often highest. As a result, the cash value may not build up substantially enough for loans for the first few years. It’s always best to check with your insurance provider to understand the specific timelines for your policy.
Is IUL a good option for retirement planning?
IUL can be a component of a comprehensive retirement plan, but it’s important to view it as a life insurance policy first, with potential retirement benefits as a secondary feature. For most people, a 401(k) or other employer-sponsored retirement plans are better primary retirement savings vehicles due to lower fees, potential employer matching, and no caps on earnings.
However, IUL can be a valuable supplemental strategy, particularly for:
- High-net-worth individuals who have already maximized contributions to other retirement accounts.
- Those looking for tax diversification in retirement, as policy loans can provide tax-free income.
- Individuals who want permanent life insurance coverage that also offers a cash value component with growth potential and downside protection.
It’s crucial to weigh the costs and complexities against the potential benefits and to ensure that the IUL aligns with your overall financial goals.
Conclusion: Is an IUL the Right Shield for Your Future?
We’ve journeyed through the A to Z of IUL – basics and education, from its mechanics and pros and cons to comparisons with other life insurance. It’s clear that Indexed Universal Life insurance is a sophisticated financial tool, offering a unique blend of lifelong protection and market-linked cash value growth with built-in downside protection.
While the potential for higher returns and tax advantages is compelling, the complexity, caps on returns, and ongoing costs require careful consideration. IUL is not a simple product, and its effectiveness hinges on a thorough understanding and diligent management.
Whether an IUL is the right shield for your future depends on your individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and long-term planning needs. We believe that education is your most powerful tool in making informed financial decisions.
At ShieldWise™, we’re committed to providing clear, jargon-free guidance to help you protect your family, control costs, and secure the right coverage. We encourage you to continue your IUL – basics and education by seeking professional advice custom to your unique circumstances. A licensed insurance agent or fiduciary advisor can help you steer the complexities and determine if an IUL policy aligns with your vision for financial security.
Ready to explore how an IUL policy could fit into your financial plan? Learn more about how an IUL policy can fit into your financial plan.
