Why Understanding Your Medicare Coverage Options Matters
A guide to understanding medicare coverage options starts with one simple truth: Medicare isn’t one-size-fits-all. When you turn 65 (or become eligible earlier due to disability), you face a choice between two main paths—Original Medicare or Medicare Advantage—and each comes with its own add-ons, trade-offs, and costs.
Here’s what you need to know right away:
- Original Medicare (Parts A & B) gives you broad doctor choice nationwide, but you’ll likely want to add Part D for prescriptions and Medigap to cover gaps
- Medicare Advantage (Part C) bundles hospital, medical, and usually drug coverage into one plan, often with extra benefits like dental and vision—but you’ll need to use the plan’s network
- Part A covers hospital stays and is free for most people
- Part B covers doctor visits and outpatient care, with a standard premium of $174.70/month in 2024
- Part D covers prescriptions and helps avoid late enrollment penalties
- Medigap is supplemental insurance that pays for costs Original Medicare doesn’t cover
More than 68 million Americans rely on Medicare, yet many feel overwhelmed by the “alphabet soup” of Parts A, B, C, and D. The good news? Once you understand the basic structure, making the right choice becomes much clearer.
You don’t have to become an insurance expert. You just need to know which questions to ask and where to find trustworthy answers.
The stakes are real. Picking the wrong plan—or missing enrollment deadlines—can mean paying more out-of-pocket, losing access to your doctors, or facing permanent penalties. But picking the right plan means predictable costs, comprehensive coverage, and peace of mind.
This guide walks you through every part of Medicare in plain English, so you can make a confident choice that fits your health needs and budget.
The “Alphabet Soup” of Medicare: Parts A, B, C, and D
Medicare, our nation’s federal health insurance program, is designed to help cover the costs of healthcare for eligible individuals. It’s primarily for those aged 65 or older, but it also extends to younger individuals with certain disabilities or medical conditions, such as End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD).
To help you steer this system, Medicare is divided into four main parts, each covering different aspects of your health needs. Think of them as building blocks that, when combined, create your complete coverage picture. Understanding these distinct parts is the first step in creating your personalized guide to understanding medicare coverage options.

Let’s explain these parts one by one. You can find more comprehensive information on the official Parts of Medicare website.
Medicare Part A: Hospital Insurance
Medicare Part A is often called “Hospital Insurance” for a good reason – it primarily covers inpatient care. This includes:
- Inpatient hospital care: When you’re admitted to a hospital for treatment.
- Skilled nursing facility care: Short-term stays in a skilled nursing facility after a hospital stay, like for rehabilitation.
- Hospice care: Support and care for terminally ill individuals.
- Some home health care: Limited home health services if you meet specific criteria.
Part A Costs: For most people, Part A is premium-free. This is because they (or their spouse) have paid Medicare taxes through payroll deductions for at least 10 years. However, even with premium-free Part A, there are still out-of-pocket costs. For 2024, the Part A deductible is $1,632 per benefit period. A benefit period begins the day you’re admitted to a hospital or skilled nursing facility and ends after you’ve been out for 60 days in a row.
Medicare Part B: Medical Insurance
Medicare Part B is your “Medical Insurance” and covers a wide range of outpatient services and supplies that Part A doesn’t. This is where most of your day-to-day medical needs come into play, including:
- Doctor visits: Your regular check-ups and specialist appointments.
- Outpatient care: Services received in a hospital outpatient department, like emergency room visits (that don’t lead to an inpatient admission).
- Preventive services: Screenings, shots, and counseling to help you stay healthy and catch problems early.
- Medical equipment: Durable medical equipment like wheelchairs, walkers, and oxygen.
- Mental health services: Outpatient mental health care.
- Ambulance services: Emergency ambulance transportation.
- Diagnostic tests: Lab tests and X-rays.
Part B Costs: Unlike Part A, most people pay a monthly premium for Part B. For 2024, the standard monthly premium for Part B is $174.70. You’ll also have an annual deductible, which is $240 for 2024. After you meet your deductible, you typically pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most doctor services and other outpatient care (this is called coinsurance). Higher-income individuals may pay a higher premium, known as the Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA).
Medicare Part C: Medicare Advantage
Medicare Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, is a different way to get your Medicare benefits. Instead of the government directly providing your coverage through Original Medicare (Parts A & B), private insurance companies approved by Medicare offer these plans.
Medicare Advantage plans must cover everything that Original Medicare covers (Parts A and B), but they often go beyond that. Many plans also include:
- Prescription drug coverage (Part D): Most Medicare Advantage plans bundle prescription drug coverage directly into the plan, so you don’t need a separate Part D plan.
- Extra benefits: These can include vision, hearing, and dental services, wellness programs, and even gym memberships.
- Out-of-pocket maximums: Unlike Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage plans have a yearly limit on your out-of-pocket costs for covered medical services.
How they work: Medicare Advantage plans often operate within networks, meaning you might need to use doctors, hospitals, and other providers that are part of the plan’s network for non-emergency care. Common plan types include:
- HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations): Generally require you to choose a primary care doctor within the plan’s network and get referrals to see specialists.
- PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations): Offer more flexibility, allowing you to see out-of-network providers, though usually at a higher cost.
While many Medicare Advantage plans may offer a $0 monthly plan premium, you still typically need to pay your Medicare Part B premium.
Medicare Part D: Prescription Drug Coverage
Medicare Part D helps cover the cost of prescription drugs. This coverage is offered through private insurance companies approved by Medicare. You can get Part D in two main ways:
- As a stand-alone plan: If you have Original Medicare (Parts A & B) and want prescription drug coverage, you can enroll in a separate Part D plan.
- As part of a Medicare Advantage plan: As we mentioned, most Medicare Advantage plans include prescription drug coverage (MAPD plans).
How Part D works: Each Part D plan has a list of covered drugs called a “formulary.” These formularies can vary significantly between plans, so it’s crucial to check if your specific medications are covered. Plans also divide drugs into “tiers” based on cost, with lower-tier drugs typically costing less.
Part D Costs: Costs for Part D plans include a monthly premium (which varies by plan), and you might have a deductible. For 2024, Part D deductibles can be up to $545. After you meet your deductible, you’ll typically pay a copayment or coinsurance for your prescriptions. Good news for your wallet: starting in 2025, all Part D plans and Medicare Advantage plans with drug coverage must cap out-of-pocket costs for covered prescription drugs at $2,000 a year.
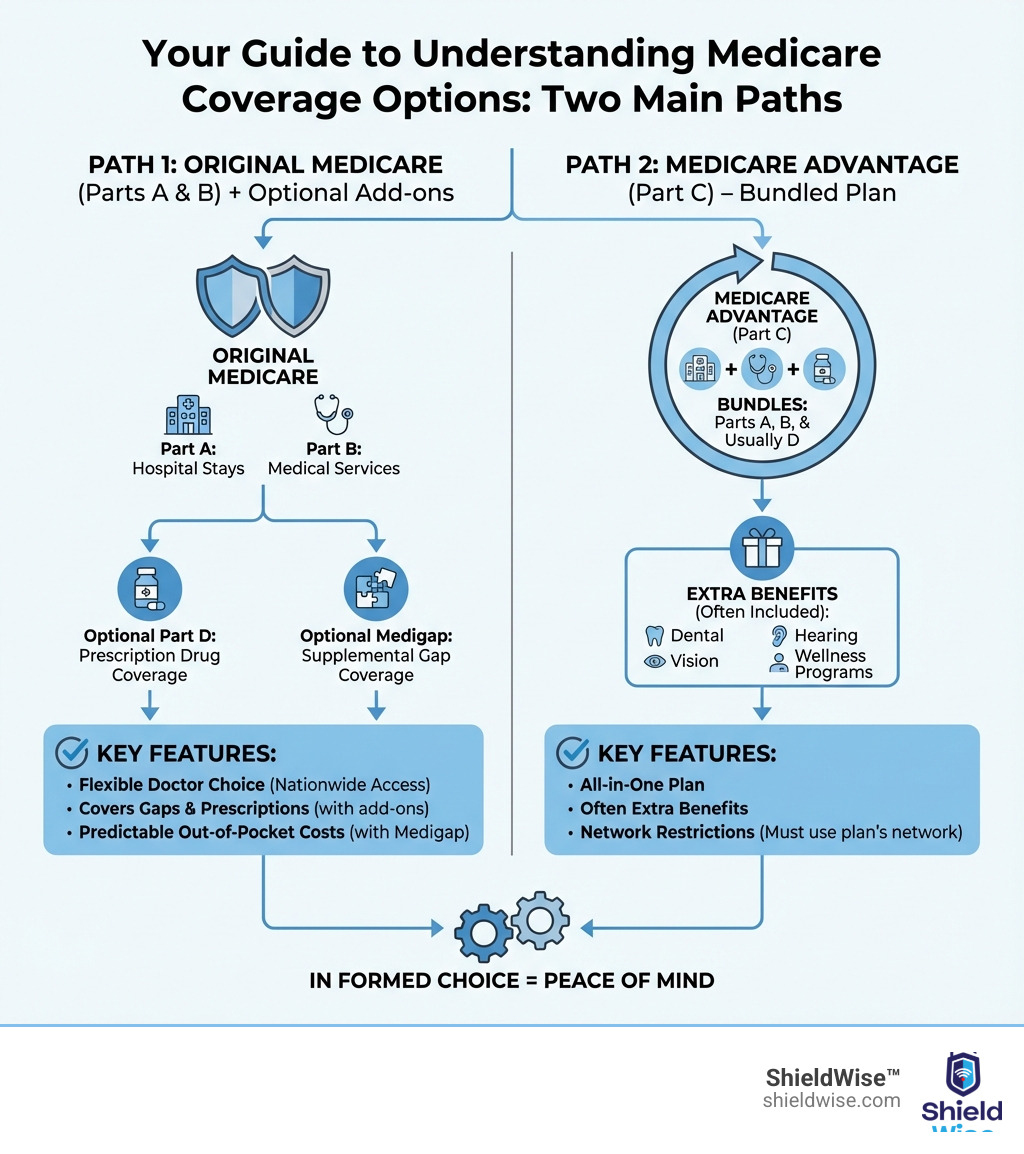
The Two Main Paths: Original Medicare vs. Medicare Advantage
Now that we’ve covered the “alphabet soup,” let’s look at the two fundamental approaches to Medicare coverage. This is often the biggest decision point in your guide to understanding medicare coverage options. We’ll help you explore which path might be the best fit for your healthcare needs and lifestyle in Illinois.
When comparing Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage, consider factors like doctor choice, costs, coverage, and even foreign travel.
- Doctor & Hospital Choice:
- Original Medicare: You can go to any doctor or hospital in the U.S. that accepts Medicare. This offers immense flexibility.
- Medicare Advantage: You’ll typically need to use doctors and hospitals within the plan’s network, and you might need referrals to see specialists, especially with HMO plans.
- Costs:
- Original Medicare: You pay your Part B premium, deductibles for Part A and B, and 20% coinsurance for most Part B services. There’s no yearly out-of-pocket limit, which is why many people add Medigap.
- Medicare Advantage: You still pay your Part B premium. The plan itself may have a separate premium (often $0). You’ll have deductibles, copays, and coinsurance that vary by plan, but there’s a yearly out-of-pocket maximum.
- Coverage:
- Original Medicare: Covers medically necessary hospital and medical services. You’ll need to add a separate Part D plan for prescription drugs.
- Medicare Advantage: Covers all medically necessary services Original Medicare covers, often includes Part D, and may offer extra benefits like routine dental, vision, and hearing care.
- Foreign Travel:
- Original Medicare: Generally doesn’t cover medical care outside the U.S. (exceptions are very limited).
- Medicare Advantage: Most plans also don’t cover care outside the U.S., but some may offer emergency coverage when traveling abroad. If international travel is a significant part of your retirement plans, travel health insurance is highly recommended regardless of your Medicare choice.
Choosing Original Medicare (Parts A & B)
If you value flexibility and nationwide access to doctors and hospitals that accept Medicare, Original Medicare might be your preferred path. With Original Medicare:
- Freedom to choose doctors: You can see any doctor, specialist, or hospital in the U.S. that accepts Medicare, without needing a referral. This is a huge plus for many, especially if you have established relationships with specific providers.
- Nationwide coverage: Whether you’re at home in Illinois or traveling across the country, your coverage remains consistent.
- Predictable coverage for core services: Original Medicare sets clear guidelines for what’s covered under medically necessary services.
To make Original Medicare more comprehensive, most people choose to pair it with:
- Medicare Part D: For prescription drug coverage.
- Medicare Supplement Insurance (Medigap): To help cover the “gaps” in Original Medicare, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
This combination offers robust coverage with maximum provider choice, but it typically means managing multiple plans. For a deeper dive into the fundamentals, explore our More info about Medicare basics guide.
Choosing Medicare Advantage (Part C)
If you prefer an all-in-one approach with potentially lower monthly premiums and an annual cap on out-of-pocket costs, Medicare Advantage could be a great fit. With these plans:
- All-in-one convenience: Most plans bundle your hospital, medical, and prescription drug coverage (Parts A, B, and D) into a single plan. Many also offer extra benefits like routine dental, vision, and hearing.
- Lower premiums (often $0): While you’ll still pay your Part B premium, many Medicare Advantage plans have a $0 monthly premium for the plan itself.
- Annual out-of-pocket limit: This provides peace of mind, knowing there’s a maximum amount you’ll pay for covered medical services in a year.
- Includes extra benefits: Many plans offer valuable benefits not covered by Original Medicare, such as gym memberships, transportation to appointments, and even healthy food allowances.
However, be aware of:
- Network limitations: You’ll generally need to use doctors and facilities within the plan’s network. If you go out of network, services might not be covered, or you’ll pay more.
- May require referrals: Depending on the plan type (e.g., HMO), you might need a referral from your primary care physician to see a specialist.
The choice largely depends on your priorities: do you prefer maximum flexibility (Original Medicare) or bundled benefits and cost predictability (Medicare Advantage)? We encourage you to Compare Original Medicare & Medicare Advantage directly on Medicare’s official website.
Your Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Medicare Coverage Options
Making an informed decision about your Medicare coverage isn’t just about picking a plan; it’s about customizing your healthcare to fit your life. This comprehensive guide to understanding medicare coverage options digs into crucial aspects like supplemental insurance, enrollment timelines, and how Medicare interacts with other forms of coverage. By understanding these details, you can avoid penalties and ensure your coverage truly works for you.
A beginner’s guide to understanding Medicare coverage options: Medigap
If you choose Original Medicare (Parts A & B), you’ll quickly find that while it covers a lot, it doesn’t cover everything. That’s where Medicare Supplement Insurance, commonly known as Medigap, comes in. Medigap policies are sold by private companies and are designed to “fill the gaps” in your Original Medicare coverage.
What does “fill the gaps” mean? It means Medigap helps pay for some of the out-of-pocket costs that Original Medicare leaves behind, such as:
- Part A and Part B deductibles
- Part A and Part B coinsurance
- Extended hospital stays
- Blood transfusions
Standardized Plans: Medigap policies are standardized, meaning the benefits for each plan letter (e.g., Plan G, Plan K) are the same regardless of which insurance company sells it. In most states, there are 10 different standardized Medigap plans available. This makes comparing policies easier: you’re essentially comparing prices for the exact same benefits across different insurers. The cost of a Medigap policy depends on the plan type and the company you buy it from.
Best Time to Buy: The best time to buy a Medigap policy is during your Medigap Open Enrollment Period. This 6-month period starts the month you turn 65 and are enrolled in Medicare Part B. During this time, insurance companies must sell you any Medigap policy they offer, regardless of your health status, and they cannot charge you more due to pre-existing conditions. If you miss this window, you may pay more or not be able to buy a policy at all, depending on your health.
Medigap policies generally don’t cover long-term care, vision, dental, hearing aids, private-duty nursing, or prescription drugs. If you need prescription drug coverage with Original Medicare and Medigap, you’ll need to enroll in a separate Part D plan. Also, you cannot have a Medigap policy if you are enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan.
An advanced guide to understanding Medicare coverage options: Enrollment
Enrollment periods are critical. Missing them can lead to late enrollment penalties, higher premiums, or gaps in coverage. Knowing when you can sign up for Medicare is just as important as knowing what it covers.
Here are the key enrollment periods to keep in mind:
- Initial Enrollment Period (IEP): This is your first chance to enroll in Medicare. It’s a 7-month window that begins 3 months before your 65th birthday, includes the month you turn 65, and ends 3 months after your 65th birthday. If you’re eligible due to disability, your IEP starts after you’ve received Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits for 24 months. Enrolling during your IEP is crucial to avoid penalties.
- Open Enrollment Period (OEP): Also known as the Annual Election Period, this runs from October 15 through December 7 every year. During this time, you can:
- Switch from Original Medicare to a Medicare Advantage plan.
- Switch from a Medicare Advantage plan back to Original Medicare.
- Switch from one Medicare Advantage plan to another.
- Switch from one Part D plan to another.
- Enroll in a Part D plan if you didn’t before.
Changes made during OEP take effect on January 1 of the following year.
- Medicare Advantage Open Enrollment Period: This period runs from January 1 to March 31 each year. If you’re already in a Medicare Advantage plan, you can use this time to switch to a different Medicare Advantage plan or switch back to Original Medicare (and join a Part D plan).
- Special Enrollment Periods (SEPs): These periods occur outside of the standard enrollment times and are triggered by certain life events, such as moving to a new area, losing other health coverage (like employer-sponsored insurance), or qualifying for Extra Help.
Late Enrollment Penalties: It’s no joke; the government charges penalties for not enrolling on time.
- Part B Late Enrollment Penalty: If you don’t sign up for Part B when you’re first eligible and don’t have other creditable coverage (like employer group health insurance), your monthly premium may go up 10% for each full 12-month period you could have had Part B but didn’t. This penalty is permanent.
- Part D Late Enrollment Penalty: If you don’t join a Part D plan when you’re first eligible and go 63 days or more without other creditable prescription drug coverage, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty. This penalty is calculated by multiplying 1% of the national base beneficiary premium by the number of full months you delayed enrollment. This penalty is also permanent and added to your monthly Part D premium.
You can apply for Medicare directly through the Social Security Administration website or by calling them.
How Medicare Coordinates with Other Insurance
Many individuals have other forms of health insurance in addition to Medicare, such as employer-sponsored plans, COBRA, or VA benefits. Understanding how Medicare coordinates with these plans is crucial to ensure you have comprehensive coverage and avoid unexpected costs. The general rule is to determine which plan is the “primary payer” (pays first) and which is the “secondary payer” (pays second).
- Employer-Sponsored Plans: If you’re still working past 65 and have health insurance through your (or your spouse’s) employer, how Medicare coordinates depends on the size of the employer.
- Large Employer (20 or more employees): Your employer plan is typically the primary payer, and Medicare is secondary. In this scenario, you might be able to delay enrolling in Part B without penalty.
- Small Employer (fewer than 20 employees): Medicare is usually the primary payer, and your employer plan is secondary. You should enroll in Part B when first eligible to avoid penalties.
It’s always best to speak with your employer’s HR department to understand how their plan works with Medicare.
- COBRA: If you have COBRA coverage, Medicare usually pays first, and COBRA pays second. COBRA is generally not considered “creditable coverage” that allows you to delay Part B enrollment without penalty.
- VA Benefits: If you have health benefits through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), these benefits can work alongside Medicare. However, VA benefits only cover care received at VA facilities. Medicare covers care received outside the VA system. It’s often recommended to enroll in both Part A and Part B if you have VA benefits to ensure broader coverage options.
- TRICARE: If you have TRICARE (for military members, retirees, and their families), you generally need to have Medicare Parts A and B to maintain your TRICARE coverage once you become eligible for Medicare.
Understanding this coordination can be complex, and individual situations vary. Always confirm with your benefits administrator or Medicare directly to ensure you have the right coverage mix.
Where to Find Unbiased Help and Resources
Navigating the nuances of Medicare can feel like a full-time job. But you don’t have to go it alone. There are fantastic, unbiased resources available to help you understand your options and make confident choices. For more general guidance, remember our internal Medicare category page.
Official Government Websites
Your first stop for reliable, up-to-date Medicare information should always be the official source.
- Medicare.gov: This is the official website for Medicare, a treasure trove of information. You can browse articles, live chat with a representative, or call 1-800-MEDICARE (1-800-633-4227, TTY 877-486-2048). The site also offers powerful tools:
- Plan comparison tools: Enter your ZIP code to compare Original Medicare with Medicare Advantage plans and Part D plans available in Illinois. You can even input your specific medications to see which plans offer the best coverage and lowest costs for your prescriptions.
- Cost estimators: Get an idea of potential out-of-pocket expenses.
We highly recommend you visit www.medicare.gov to explore all these resources.
State Health Insurance Assistance Programs (SHIP)
For personalized, unbiased counseling, State Health Insurance Assistance Programs (SHIPs) are invaluable. These organizations offer free expert assistance to Medicare-eligible individuals and their families.
- Free, unbiased counseling: SHIP counselors are trained volunteers who can help you understand your Medicare options, compare plans, and answer your specific questions, all without trying to sell you anything. They are a fantastic resource for Illinois residents looking for local guidance.
- Personalized help: Whether you need help understanding enrollment periods, comparing Part D plans, or figuring out how Medigap works, SHIP can provide custom advice.
- You can Find your local SHIP now by visiting their website. This service is specifically designed to cut through the confusion and help you make the best choice for your situation.
Conclusion: Making Your Medicare Choice with Confidence
Understanding your Medicare coverage options is a journey, not a sprint. We’ve walked through the “alphabet soup” of Parts A, B, C, and D, explored the two main paths of Original Medicare versus Medicare Advantage, and highlighted the importance of Medigap, enrollment periods, and how Medicare coordinates with other insurance.
The key takeaway is empowerment through knowledge. By taking the time to learn, ask questions, and use unbiased resources, you can move from feeling overwhelmed to making a confident decision about your healthcare. Remember to review your coverage annually during the Open Enrollment Period (October 15 – December 7), as your health needs and available plans can change.
At ShieldWise™, we believe in clear, jargon-free guidance to help you compare plans and secure the right coverage. We understand that navigating Medicare can be complex, but with the right information, you can protect your health and control your costs.
Ready to take the next step? We encourage you to start exploring and comparing your options today.

